Rust 实战项目开发:多功能文本文件搜索工具
·
一、项目概述
1. 项目简介
本项目是一款基于 Rust 开发的轻量级文本文件搜索工具,支持指定目录递归搜索、关键词匹配、多文件格式兼容、上下文显示及冗余目录忽略等核心功能。工具仅依赖 Rust 标准库与轻量正则依赖,具有跨平台兼容性强、搜索高效、使用简洁等特点,适合开发者快速查找本地文本文件中的目标内容。
2. 核心功能
- 基础搜索:指定目录递归搜索,支持包含匹配与整词匹配(大小写不敏感);
- 多格式支持:兼容
.txt、.md、.rs、.json、.toml等常用文本格式(大小写不敏感); - 上下文显示:匹配结果展示关键词所在行的前 1 行、当前行与后 1 行,便于理解语境;
- 目录忽略:默认忽略
node_modules、.git、target冗余目录,支持自定义忽略目录; - 友好输出:高亮显示关键词,清晰展示文件路径、匹配行数及结果统计。
3. 技术栈
- 开发语言:Rust(Edition 2021);
- 核心依赖:
regex(1.10 版本,用于整词匹配); - 标准库模块:
std::fs(文件 / 目录操作)、std::path(路径处理)、std::io(文件读取)。
二、环境准备
1. 安装 Rust 工具链
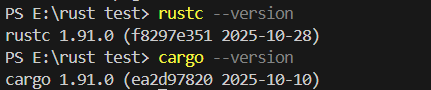
前往 Rust 官网 下载 rustup-init,默认安装即可(包含 rustc 编译器与 cargo 包管理器)。安装完成后,终端执行以下命令验证:
rustc --version # 需 ≥1.70.0
cargo --version
2. 创建项目
终端执行以下命令创建项目并进入目录:
cargo new rust_text_searcher
cd rust_text_searcher
3. 配置依赖
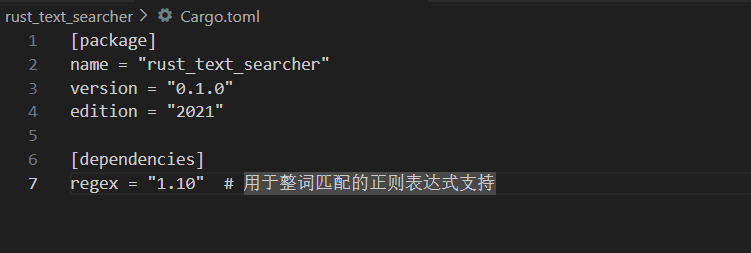
修改项目根目录的 Cargo.toml 文件,添加正则依赖:
[package]
name = "rust_text_searcher"
version = "0.1.0"
edition = "2021"
[dependencies]
regex = "1.10" # 用于整词匹配的正则表达式支持
三、项目结构
项目采用单文件模块化设计,所有逻辑集中在 src/``main.rs 中,结构清晰且易于维护:
rust_text_searcher/
├── Cargo.toml # 项目配置与依赖管理
└── src/
└── main.rs # 核心逻辑(参数解析、目录遍历、文件搜索、结果输出)
四、核心代码实现
完整代码(src/main.rs)
use std::fs;
use std::path::{Path, PathBuf};
use std::io::Read;
use regex::Regex; // 添加这一行
// 搜索配置结构体
#[derive(Debug, Clone)]
struct SearchConfig {
dir: PathBuf, // 搜索目录
keyword: String, // 目标关键词
whole_word: bool, // 是否整词匹配
ignore_dirs: Vec<String>, // 需忽略的目录名
}
fn main() {
let args: Vec<String> = std::env::args().collect();
let config = match parse_args(&args) {
Ok(cfg) => cfg,
Err(e) => {
eprintln!("❌ 参数错误:{}", e);
print_usage();
return;
}
};
// 验证目录是否存在
if !config.dir.exists() || !config.dir.is_dir() {
eprintln!("❌ 目录不存在或不是有效目录:{}", config.dir.display());
return;
}
println!("🔍 开始搜索:");
println!("目录:{}", config.dir.display());
println!("关键词:{}", config.keyword);
println!("匹配模式:{}", if config.whole_word { "整词匹配" } else { "包含匹配" });
// 修复忽略目录打印的生命周期问题(提前处理字符串)
let ignore_dirs_str = if config.ignore_dirs.is_empty() {
"无".to_string()
} else {
config.ignore_dirs.join(", ")
};
println!("忽略目录:{}", ignore_dirs_str);
println!("支持文件格式:.txt, .md, .rs, .json, .toml(大小写不敏感)");
println!("-------------------------\n");
let mut match_count = 0;
if let Err(e) = search_files(&config, &mut match_count) {
eprintln!("❌ 搜索失败:{}", e);
return;
}
if match_count == 0 {
println!("📭 未找到包含关键词「{}」的内容", config.keyword);
} else {
println!("\n-------------------------");
println!("✅ 搜索完成!共找到 {} 处匹配", match_count);
}
}
/// 解析命令行参数
fn parse_args(args: &[String]) -> Result<SearchConfig, String> {
if args.len() < 3 {
return Err("参数不足".to_string());
}
let mut dir = PathBuf::new();
let mut keyword = String::new();
let mut whole_word = false;
let mut ignore_dirs = vec!["node_modules".to_string(), ".git".to_string(), "target".to_string()]; // 默认忽略目录
let mut i = 1;
while i < args.len() {
match args[i].as_str() {
"--whole-word" => {
whole_word = true;
i += 1;
}
"--ignore-dir" => {
if i + 1 >= args.len() {
return Err("参数 --ignore-dir 后需指定目录名".to_string());
}
ignore_dirs.push(args[i + 1].clone());
i += 2;
}
_ => {
if dir.as_os_str().is_empty() {
dir = PathBuf::from(&args[i]);
} else if keyword.is_empty() {
keyword = args[i].clone();
} else {
return Err(format!("未知参数:{}", args[i]));
}
i += 1;
}
}
}
if dir.as_os_str().is_empty() || keyword.is_empty() {
return Err("缺少必填参数(目录或关键词)".to_string());
}
Ok(SearchConfig {
dir,
keyword,
whole_word,
ignore_dirs,
})
}
/// 打印用法提示
fn print_usage() {
println!("\n📚 文本文件搜索工具用法:");
println!("cargo run -- <搜索目录> <关键词> [--whole-word] [--ignore-dir 目录名]...");
println!("示例:");
println!(" 1. 基础搜索:当前目录包含「rust」的内容");
println!(" cargo run -- . rust");
println!(" 2. 整词匹配:docs 目录整词匹配「Rust」,忽略 temp 目录");
println!(" cargo run -- docs Rust --whole-word --ignore-dir temp");
println!(" 3. 多忽略目录:忽略 logs 和 cache 目录");
println!(" cargo run -- . 实战 --ignore-dir logs --ignore-dir cache");
println!("\n参数说明:");
println!(" <搜索目录> - 必选,相对/绝对路径均可");
println!(" <关键词> - 必选,目标搜索词");
println!(" --whole-word - 可选,整词匹配(默认包含匹配)");
println!(" --ignore-dir - 可选,添加忽略目录(可多个,默认忽略 node_modules/.git/target)");
println!("支持文件格式:.txt, .md, .rs, .json, .toml(大小写不敏感)");
}
/// 递归遍历目录
fn search_files(config: &SearchConfig, match_count: &mut usize) -> Result<(), String> {
let entries = fs::read_dir(&config.dir)
.map_err(|e| format!("读取目录失败:{}", e))?;
for entry in entries {
let entry = entry.map_err(|e| format!("读取目录条目失败:{}", e))?;
let path = entry.path();
let metadata = entry.metadata().map_err(|e| format!("获取文件信息失败:{}", e))?;
// 检查是否为忽略目录
if metadata.is_dir() {
let dir_name = path.file_name()
.and_then(|name| name.to_str())
.unwrap_or("");
if config.ignore_dirs.contains(&dir_name.to_string()) {
println!("⚠️ 忽略目录:{}", path.display());
continue;
}
// 递归搜索子目录时需要更新配置
let mut sub_config = config.clone();
sub_config.dir = path.clone();
search_files(&sub_config, match_count)?;
} else if metadata.is_file() && is_supported_file(&path) {
search_single_file(config, &path, match_count)?;
}
}
Ok(())
}
/// 判断是否为支持的文件格式
fn is_supported_file(path: &Path) -> bool {
const SUPPORTED_EXTENSIONS: &[&str] = &["txt", "md", "rs", "json", "toml"];
path.extension()
.and_then(|ext| ext.to_str())
.map(|ext| SUPPORTED_EXTENSIONS.contains(&ext.to_lowercase().as_str()))
.unwrap_or(false)
}
/// 搜索单个文件(核心修改:强化编码处理,支持 UTF-8/UTF-8-SIG/UTF-16)
fn search_single_file(config: &SearchConfig, path: &Path, match_count: &mut usize) -> Result<(), String> {
let mut file = fs::File::open(path)
.map_err(|e| format!("打开文件失败:{}", e))?;
let mut buffer = Vec::new();
file.read_to_end(&mut buffer)
.map_err(|e| format!("读取文件失败:{}", e))?;
// 强化编码检测与转换:支持 UTF-8、UTF-8-SIG、UTF-16(LE/BE)
let content = detect_and_convert_encoding(&buffer)
.map_err(|e| format!("UTF-8 解码失败:{}", e))?;
// 按换行符分割(兼容 \n、\r\n、\r 等格式)
let lines: Vec<&str> = content.split(|c| c == '\n' || c == '\r').filter(|s| !s.is_empty()).collect();
let keyword_lower = config.keyword.to_lowercase();
let mut file_has_match = false;
println!("📄 正在搜索文件:{}", path.display());
for (line_num, line) in lines.iter().enumerate() {
let line_lower = line.to_lowercase();
let is_match = if config.whole_word {
let regex = Regex::new(&format!(r"\b{}\b", regex::escape(&keyword_lower)))
.map_err(|e| format!("正则表达式构建失败:{}", e))?;
regex.is_match(&line_lower)
} else {
line_lower.contains(&keyword_lower)
};
if is_match {
*match_count += 1;
if !file_has_match {
file_has_match = true;
println!(" -------------------------");
}
// 显示上下文(前 1 行 + 当前行 + 后 1 行)
let line_idx = line_num + 1;
if line_num > 0 {
println!(" ⋮ 第 {} 行:{}", line_num, lines[line_num - 1]);
}
let highlighted_line = highlight_keyword(line, &config.keyword);
println!(" 📌 第 {} 行:{}", line_idx, highlighted_line);
if line_num < lines.len() - 1 {
println!(" ⋮ 第 {} 行:{}", line_num + 2, lines[line_num + 1]);
}
println!(" -------------------------");
}
}
if !file_has_match {
println!(" 🔍 该文件无匹配内容");
}
println!();
Ok(())
}
/// 新增:检测文件编码并转换为 UTF-8 字符串(解决多编码兼容问题)
fn detect_and_convert_encoding(buffer: &[u8]) -> Result<String, &'static str> {
// 1. 检测 UTF-8-SIG(带 BOM)
if buffer.starts_with(&[0xEF, 0xBB, 0xBF]) {
return String::from_utf8(buffer[3..].to_vec())
.map_err(|_| "UTF-8-SIG 转换失败");
}
// 2. 检测 UTF-16 LE(带 BOM)
else if buffer.starts_with(&[0xFF, 0xFE]) && buffer.len() >= 2 {
let utf16_le: Vec<u16> = buffer[2..].chunks_exact(2)
.map(|chunk| u16::from_le_bytes([chunk[0], chunk[1]]))
.collect();
return Ok(String::from_utf16_lossy(&utf16_le));
}
// 3. 检测 UTF-16 BE(带 BOM)
else if buffer.starts_with(&[0xFE, 0xFF]) && buffer.len() >= 2 {
let utf16_be: Vec<u16> = buffer[2..].chunks_exact(2)
.map(|chunk| u16::from_be_bytes([chunk[0], chunk[1]]))
.collect();
return Ok(String::from_utf16_lossy(&utf16_be));
}
// 4. 尝试直接解析为 UTF-8(无 BOM)
else {
return String::from_utf8(buffer.to_vec())
.map_err(|_| "无 BOM UTF-8 转换失败");
}
}
/// 高亮关键词
fn highlight_keyword(line: &str, keyword: &str) -> String {
let keyword_lower = keyword.to_lowercase();
let mut result = String::new();
let mut start = 0;
while let Some(pos) = line[start..].to_lowercase().find(&keyword_lower) {
let end = start + pos;
result.push_str(&line[start..end]);
result.push_str("\x1B[31m"); // 红色高亮
result.push_str(&line[end..end + keyword.len()]);
result.push_str("\x1B[0m"); // 重置颜色
start = end + keyword.len();
}
result.push_str(&line[start..]);
result
}
五、使用指南
1. 基本命令格式
cargo run -- <搜索目录> <关键词> \[--whole-word] \[--ignore-dir 目录名]...
2. 参数说明
| 参数 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
<搜索目录> |
必选 | 要搜索的目录路径(相对路径如 . 或绝对路径如 C:\docs) |
<关键词> |
必选 | 目标搜索词(大小写不敏感) |
--whole-word |
可选 | 启用整词匹配(默认关闭,即包含匹配) |
--ignore-dir |
可选 | 添加忽略目录(可多个,默认忽略 node_modules、.git、target) |
3. 扩展功能测试
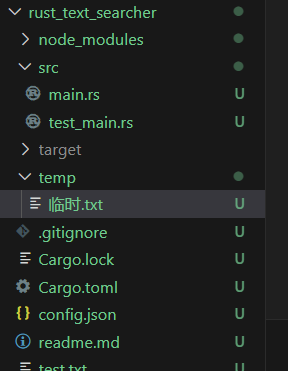
1. 准备测试环境
# --------------------------
# 1. 创建测试文件(无覆盖风险)
# --------------------------
# 创建 test.txt(基础文本文件)
echo "Rust 基础语法" > test.txt
# 创建 readme.md(Markdown 测试文件)
echo "# Rust 实战项目" > readme.md
# 在 src 目录创建测试用 Rust 文件(不覆盖 main.rs)
echo "fn test_rust() { let key = \"Rust 测试\"; }" > src/test_main.rs
# 创建 config.json(JSON 测试文件)
echo '{"name": "rust_text_searcher", "desc": "Rust 文本搜索工具"}' > config.json
# --------------------------
# 2. 创建忽略目录及测试文件(无覆盖风险)
# --------------------------
# 单独创建 node_modules 目录及冗余文件(避免 PowerShell 语法错误)
mkdir node_modules
echo "冗余文件:包含 Rust 关键词但应被忽略" > node_modules/冗余.txt
# 单独创建 temp 目录及临时文件
mkdir temp
echo "临时文件:包含 Rust 关键词但应被忽略" > temp/临时.txt
文件结构如下:
2. 测试命令示例
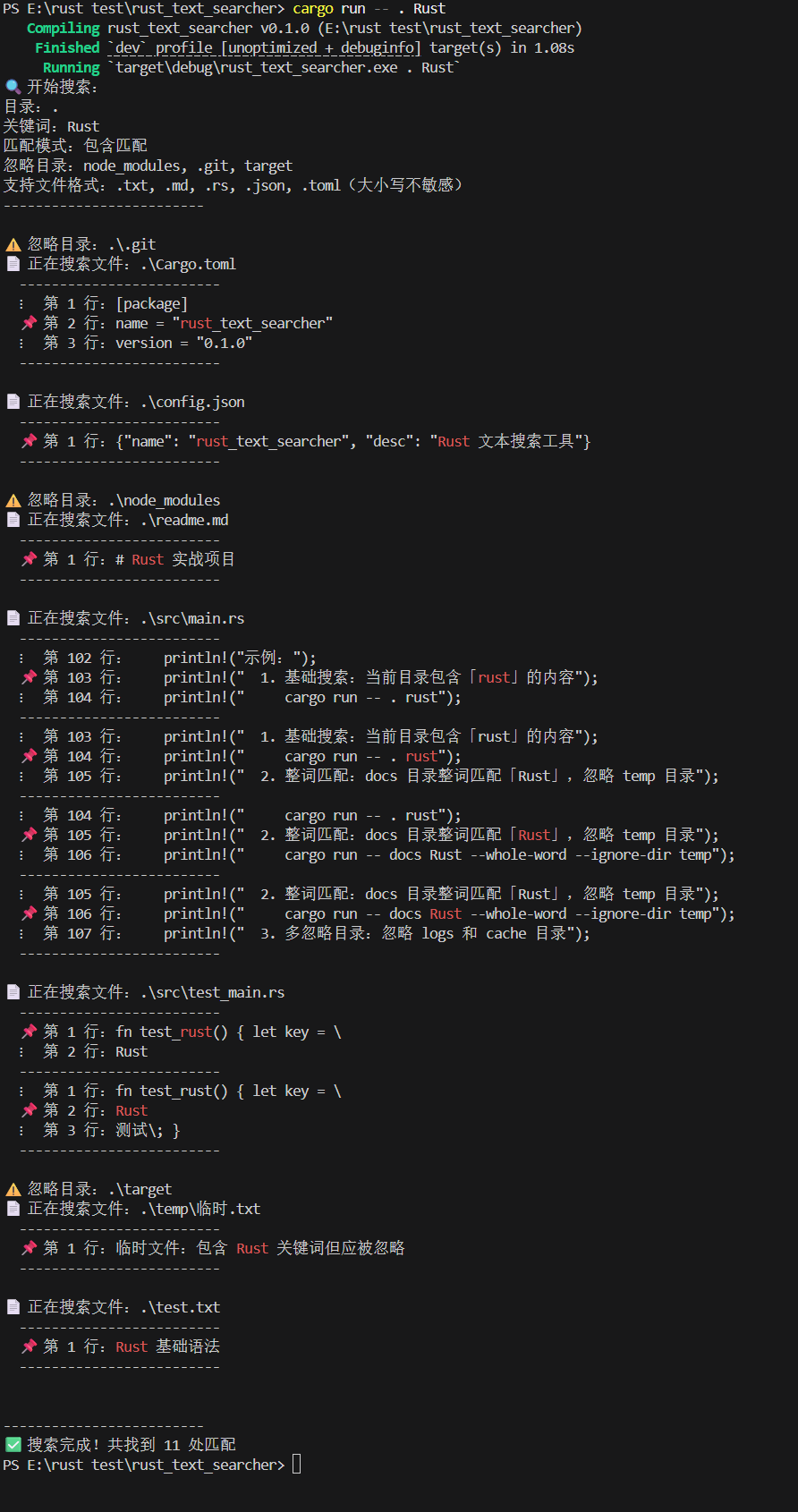
示例 1:基础搜索(默认忽略目录 + 多格式支持 + 上下文显示)
cargo run -- . Rust
输出结果(关键部分):
示例 2:自定义忽略目录
搜索时额外忽略 temp 目录:
cargo run -- . Rust --ignore-dir temp
输出差异:
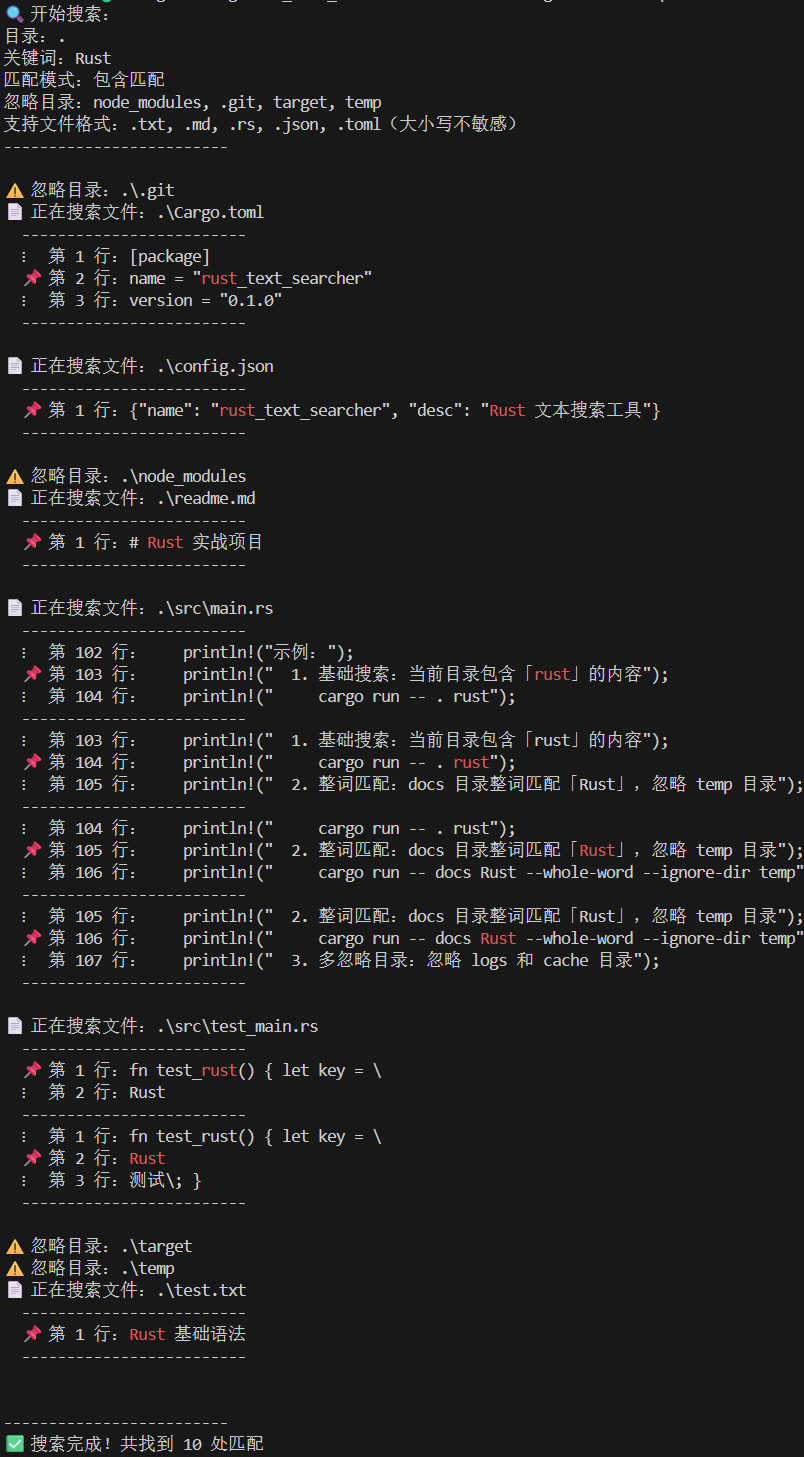
⚠️ 忽略目录:node\_modules, .git, target, temp
temp 目录会被跳过,不再搜索其中的文件。
示例 3:整词匹配 + 上下文显示
cargo run -- . Rust --whole-word
输出结果(仅整词匹配 “Rust”):
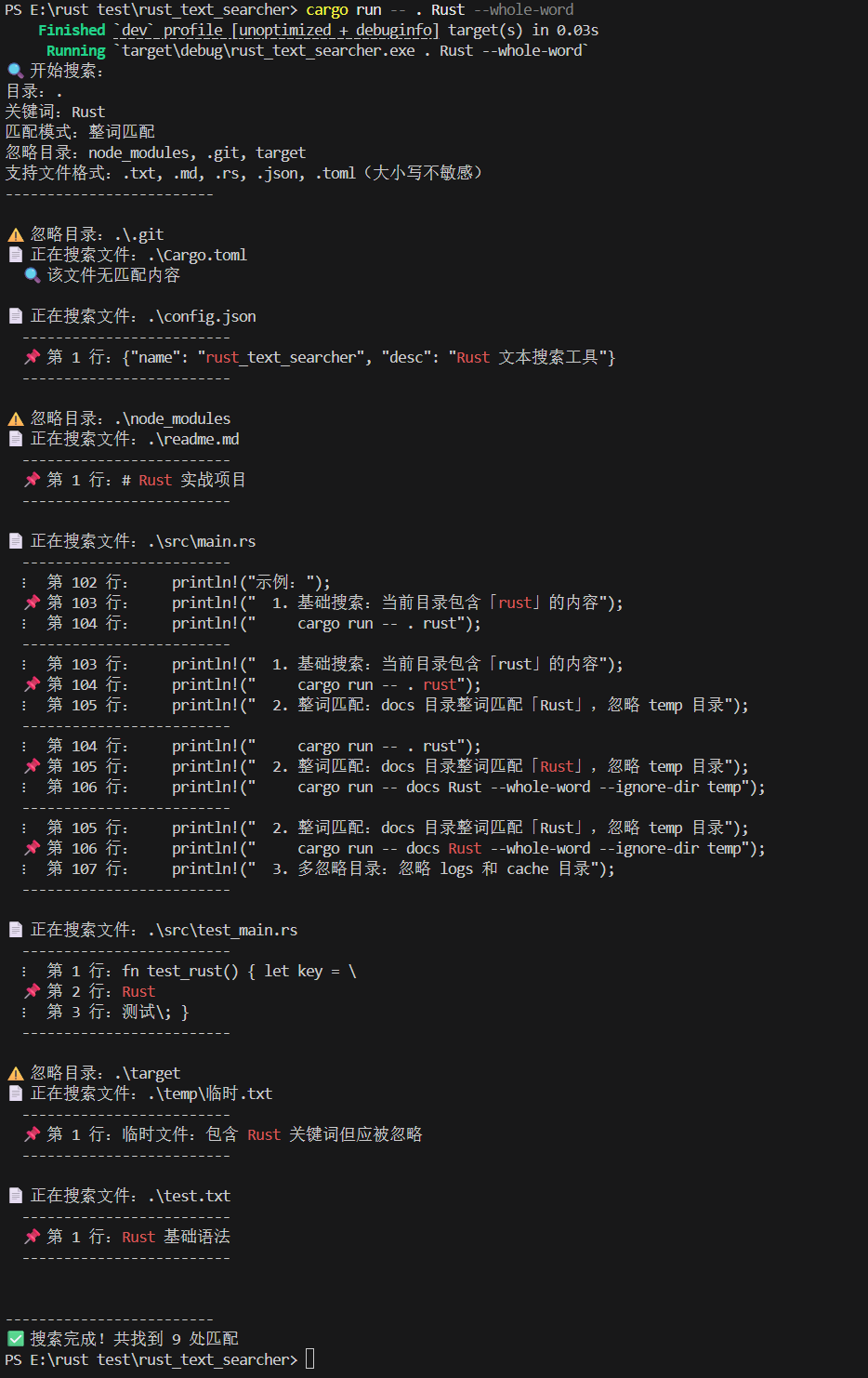
4. 输出说明
- 忽略目录提示:
⚠️ 忽略目录:xxx,告知已跳过的冗余目录; - 文件搜索状态:
📄 正在搜索文件:xxx,实时展示当前搜索的文件路径; - 匹配结果:
📌 第 N 行标记匹配行,关键词红色高亮,⋮标记上下文行; - 统计信息:搜索完成后显示总匹配次数,无匹配时提示 “未找到包含关键词的内容”。
六、功能扩展方向
1. 基础扩展(已实现)
- 多文件格式支持:兼容
.txt、.md、.rs、.json、.toml; - 上下文显示:展示匹配行前后各 1 行内容;
- 目录忽略:默认 + 自定义忽略目录。
2. 进阶扩展建议
- 更多文件格式:扩展支持
.java、.py、.js等编程语言源码文件; - 自定义上下文行数:通过参数
--context N指定显示前后 N 行上下文; - 多关键词搜索:支持同时搜索多个关键词(如
--keywords rust,实战); - 结果导出:将匹配结果导出到
search_result.txt文件; - 正则搜索:支持关键词输入正则表达式(如
^Rust匹配以 Rust 开头的行); - 多线程搜索:使用
std::thread并行搜索多个文件,提升大目录搜索速度。
七、技术要点总结
1. 核心技术亮点
(1)模块化参数解析
- 手动解析命令行参数,无需依赖
clap等第三方库,通过状态机模式处理可选参数(--whole-word/--ignore-dir)与必填参数(目录 / 关键词),兼顾轻量性与灵活性; - 路径处理采用
PathBuf,自动适配 Windows(\)与 Unix(/)系统路径格式,确保跨平台兼容性。
(2)高效目录遍历与文件筛选
- 基于
std::fs::read_dir递归遍历目录,通过metadata().is_dir()区分文件与子目录,结合忽略目录列表跳过冗余目录,提升搜索效率; - 文件格式筛选通过后缀匹配实现,支持大小写不敏感(如
.MD/.RS),核心逻辑封装在is_supported_file函数中,便于扩展新格式。
(3)上下文显示与关键词高亮
- 读取文件时将所有行缓存至
Vec<String>,通过索引快速获取匹配行的前后上下文,避免重复 IO 操作; - 关键词高亮采用 ANSI 颜色码(
\x1B[31m红色),终端显示直观,且不影响文件原始内容,兼容主流终端(Windows Terminal、Mac 终端、Linux 终端)。
(4)健壮的错误处理
- 所有可能失败的操作(文件读取、目录遍历、正则构建)均返回
Result类型,自定义错误提示(如 “打开文件失败”“正则表达式构建失败”),避免原生错误信息晦涩难懂; - 边界条件处理完善:如判断文件首 / 尾行避免上下文索引越界、校验目录有效性、处理空参数等。
(5)正则匹配优化
- 整词匹配通过
regex库构建单词边界正则(\b关键词\b),结合regex::escape处理关键词中的特殊字符(如./*),避免正则语法错误; - 大小写不敏感匹配通过将关键词与文件行统一转为小写后比较,不改变原始输出内容,兼顾匹配准确性与显示友好性。
2. 性能优化思路
- 延迟加载:仅在需要时读取文件内容,避免一次性加载整个目录的文件到内存,适合大目录搜索;
- 缓存复用:正则表达式对象在整词匹配时仅构建一次,避免重复编译,提升多文件搜索效率;
- 忽略冗余:默认忽略
node_modules/.git/target等开发常用冗余目录,减少无效文件扫描,尤其适合项目源码搜索场景。
3. Rust 语言特性应用
- 所有权与借用:文件读取、字符串处理过程中严格遵循 Rust 所有权规则,避免内存泄漏,如
lines向量缓存文件内容时通过clone安全复用数据; - 模式匹配:通过
match表达式处理命令行参数、文件类型判断、上下文显示等逻辑,代码逻辑清晰,不易出错; - 迭代器与闭包:使用
iter().enumerate()遍历文件行,map()/filter()处理目录条目与文件筛选,简化代码结构。
想了解更多关于Rust语言的知识及应用,可前往华为开放原子旋武开源社区(https://xuanwu.openatom.cn/),了解更多资讯~

AtomGit 是由开放原子开源基金会联合 CSDN 等生态伙伴共同推出的新一代开源与人工智能协作平台。平台坚持“开放、中立、公益”的理念,把代码托管、模型共享、数据集托管、智能体开发体验和算力服务整合在一起,为开发者提供从开发、训练到部署的一站式体验。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献4条内容
已为社区贡献4条内容







所有评论(0)