Linux完整备份工具 - dump, restore(现在基本不用这两个)
linux-dash
A beautiful web dashboard for Linux
项目地址:https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/li/linux-dash
·
dump
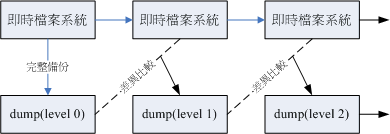
其实 dump 的功能颇强,他除了可以备份整个文件系统之外,还可以制定等级喔!什么意思啊! 假设你的 /home 是独立的一个文件系统,那你第一次进行过 dump 后,再进行第二次 dump 时, 你可以指定不同的备份等级,假如指定等级为 1 时,此时新备份的数据只会记录与第一次备份所有差异的文件而已。 看不懂吗?没关系!我们用一张简图来说明。
如上图所示,上方的『即时文件系统』是一直随著时间而变化的数据,例如在 /home 里面的文件数据会一直变化一样。 而底下的方块则是 dump 备份起来的数据,第一次备份时使用的是 level 0 ,这个等级也是完整的备份啦! 等到第二次备份时,即时文件系统内的数据已经与 level 0 不一样了,而 level 1 仅只是比较目前的文件系统与 level 0 之间的差异后,备份有变化过的文件而已。至於 level 2 则是与 level 1 进行比较。
dump 的选项虽然非常的繁复,不过如果只是想要简单的操作时,您只要记得底下的几个选项就很够用了!
[root@www ~]# dump [-Suvj] [-level] [-f 备份档] 待备份数据 [root@www ~]# dump -W 选项与参数: -S :仅列出后面的待备份数据需要多少磁碟空间才能够备份完毕; -u :将这次 dump 的时间记录到 /etc/dumpdates 文件中; -v :将 dump 的文件过程显示出来; -j :加入 bzip2 的支持!将数据进行压缩,默认 bzip2 压缩等级为 2 -level:就是我们谈到的等级,从 -0 ~ -9 共十个等级; -f :有点类似 tar 啦!后面接产生的文件,亦可接例如 /dev/st0 装置档名等 -W :列出在 /etc/fstab 里面的具有 dump 配置的 partition 是否有备份过? |
# 1. 先找出系统中最小的那个文件系统,如下所示: [root@www ~]# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/hdc2 9.5G 3.7G 5.3G 42% / /dev/hdc3 4.8G 651M 3.9G 15% /home /dev/hdc1 99M 11M 83M 12% /boot <==看起来最小的就是他啦! tmpfs 363M 0 363M 0% /dev/shm # 2. 先测试一下,如果要备份此文件系统,需多少容量? [root@www ~]# dump -S /dev/hdc1 5630976 <==注意一下,这个单位是 bytes ,所以差不多是 5.6MBytes。 # 3. 将完整备份的档名记录成为 /root/boot.dump ,同时升级记录档: [root@www ~]# dump -0u -f /root/boot.dump /boot DUMP: Date of this level 0 dump: Tue Dec 2 02:53:45 2008 <==记录等级与备份时间 DUMP: Dumping /dev/hdc1 (/boot) to /root/boot.dump <==dump的来源与目标 DUMP: Label: /boot <==文件系统的 label DUMP: Writing 10 Kilobyte records DUMP: mapping (Pass I) [regular files] <==开始进行文件对应 DUMP: mapping (Pass II) [directories] DUMP: estimated 5499 blocks. <==评估整体block数量 DUMP: Volume 1 started with block 1 at: Tue Dec 2 02:53:46 2008 DUMP: dumping (Pass III) [directories] <==开始 dump 工作 DUMP: dumping (Pass IV) [regular files] DUMP: Closing /root/boot.dump <==结束写入备份档 DUMP: Volume 1 completed at: Tue Dec 2 02:53:47 2008 DUMP: Volume 1 5550 blocks (5.42MB) <==最终备份数据容量 DUMP: Volume 1 took 0:00:01 DUMP: Volume 1 transfer rate: 5550 kB/s DUMP: 5550 blocks (5.42MB) on 1 volume(s) DUMP: finished in 1 seconds, throughput 5550 kBytes/sec DUMP: Date of this level 0 dump: Tue Dec 2 02:53:45 2008 DUMP: Date this dump completed: Tue Dec 2 02:53:47 2008 DUMP: Average transfer rate: 5550 kB/s DUMP: DUMP IS DONE # 在命令的下达方面,dump 后面接 /boot 或 /dev/hdc1 都可以的! # 而运行 dump 的过程中会出现如上的一些信息,您可以自行仔细的观察! [root@www ~]# ll /root/boot.dump /etc/dumpdates -rw-rw-r-- 1 root disk 43 Dec 2 02:53 /etc/dumpdates -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5683200 Dec 2 02:53 /root/boot.dump # 由於加上 -u 的选项,因此 /etc/dumpdates 该文件的内容会被升级!注意, # 这个文件仅有在 dump 完整的文件系统时才有支持主动升级的功能。 # 4. 观察一下系统主动创建的记录档: [root@www ~]# cat /etc/dumpdates /dev/hdc1 0 Tue Dec 2 02:53:47 2008 +0800 [文件系统] [等级] [ ctime 的时间 ] |
# 0. 看一下有没有任何文件系统被 dump 过的数据? [root@www ~]# dump -W Last dump(s) done (Dump '>' file systems): > /dev/hdc2 ( /) Last dump: never > /dev/hdc3 ( /home) Last dump: never /dev/hdc1 ( /boot) Last dump: Level 0, Date Tue Dec 2 02:53:47 2008 # 如上列的结果,该结果会捉出 /etc/fstab 里面第五栏位配置有需要 dump 的 # partition,然后与 /etc/dumpdates 进行比对,可以得到上面的结果啦! # 尤其是第三行,可以显示我们曾经对 /dev/hdc1 进行过 dump 的备份动作喔! # 1. 先恶搞一下,创建一个大约 10 MB 的文件在 /boot 内: [root@www ~]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/boot/testing.img bs=1M count=10 10+0 records in 10+0 records out 10485760 bytes (10 MB) copied, 0.166128 seconds, 63.1 MB/s # 2. 开始创建差异备份档,此时我们使用 level 1 吧: [root@www ~]# dump -1u -f /root/boot.dump.1 /boot ....(中间省略).... [root@www ~]# ll /root/boot* -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5683200 Dec 2 02:53 /root/boot.dump -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 10547200 Dec 2 02:56 /root/boot.dump.1 # 看看文件大小,岂不是就是刚刚我们所创建的那个大文件的容量吗? ^_^ # 3. 最后再看一下是否有记录 level 1 备份的时间点呢? [root@www ~]# dump -W Last dump(s) done (Dump '>' file systems): > /dev/hdc2 ( /) Last dump: never > /dev/hdc3 ( /home) Last dump: never > /dev/hdc1 ( /boot) Last dump: Level 1, Date Tue Dec 2 02:56:33 2008 ....(中间省略).... |
用 dump 备份非文件系统,亦即单一目录的方法
# 让我们将 /etc 整个目录透过 dump 进行备份,且含压缩功能 [root@www ~]# dump -0j -f /root/etc.dump.bz2 /etc DUMP: Date of this level 0 dump: Tue Dec 2 12:08:22 2008 DUMP: Dumping /dev/hdc2 (/ (dir etc)) to /root/etc.dump.bz2 DUMP: Label: /1 DUMP: Writing 10 Kilobyte records DUMP: Compressing output at compression level 2 (bzlib) DUMP: mapping (Pass I) [regular files] DUMP: mapping (Pass II) [directories] DUMP: estimated 115343 blocks. DUMP: Volume 1 started with block 1 at: Tue Dec 2 12:08:23 2008 DUMP: dumping (Pass III) [directories] DUMP: dumping (Pass IV) [regular files] DUMP: Closing /root/etc.dump.bz2 DUMP: Volume 1 completed at: Tue Dec 2 12:09:49 2008 DUMP: Volume 1 took 0:01:26 DUMP: Volume 1 transfer rate: 218 kB/s DUMP: Volume 1 124680kB uncompressed, 18752kB compressed, 6.649:1 DUMP: 124680 blocks (121.76MB) on 1 volume(s) DUMP: finished in 86 seconds, throughput 1449 kBytes/sec DUMP: Date of this level 0 dump: Tue Dec 2 12:08:22 2008 DUMP: Date this dump completed: Tue Dec 2 12:09:49 2008 DUMP: Average transfer rate: 218 kB/s DUMP: Wrote 124680kB uncompressed, 18752kB compressed, 6.649:1 DUMP: DUMP IS DONE # 上面特殊字体的部分显示:原本有 124680kb 的容量,被压缩成为 18752kb, # 整个压缩比为 6.649:1 ,还可以的压缩情况啦! |
restore
[root@www ~]# restore -t [-f dumpfile] [-h] <==用来察看 dump 档 [root@www ~]# restore -C [-f dumpfile] [-D 挂载点] <==比较dump与实际文件 [root@www ~]# restore -i [-f dumpfile] <==进入互动模式 [root@www ~]# restore -r [-f dumpfile] <==还原整个文件系统 选项与参数: 相关的各种模式,各种模式无法混用喔!例如不可以写 -tC 啦! -t :此模式用在察看 dump 起来的备份档中含有什么重要数据!类似 tar -t 功能; -C :此模式可以将 dump 内的数据拿出来跟实际的文件系统做比较, 最终会列出『在 dump 文件内有记录的,且目前文件系统不一样』的文件; -i :进入互动模式,可以仅还原部分文件,用在 dump 目录时的还原! -r :将整个 filesystem 还原的一种模式,用在还原针对文件系统的 dump 备份; 其他较常用到的选项功能: -h :察看完整备份数据中的 inode 与文件系统 label 等资讯 -f :后面就接你要处理的那个 dump 文件罗! -D :与 -C 进行搭配,可以查出后面接的挂载点与 dump 内有不同的文件! |
用 restore 观察 dump 后的备份数据内容
[root@www ~]# restore -t -f /root/boot.dump Dump date: Tue Dec 2 02:53:45 2008 <==说明备份的日期 Dumped from: the epoch Level 0 dump of /boot on www.vbird.tsai:/dev/hdc1 <==说明 level 状态 Label: /boot <==说明该 filesystem 的表头! 2 . 11 ./lost+found 2009 ./grub 2011 ./grub/grub.conf ....底下省略.... [root@www ~]# restore -t -f /root/etc.dump Dump tape is compressed. <==加注说明数据有压缩 Dump date: Tue Dec 2 12:08:22 2008 Dumped from: the epoch Level 0 dump of / (dir etc) on www.vbird.tsai:/dev/hdc2 <==是目录! Label: /1 2 . 1912545 ./etc 1912549 ./etc/rpm 1912550 ./etc/rpm/platform ....底下省略.... |
比较差异并且还原整个文件系统
# 0. 先尝试变更文件系统的内容: [root@www ~]# cd /boot [root@www boot]# mv config-2.6.18-128.el5 config-2.6.18-128.el5-back # 1. 看使进行文件系统与备份文件之间的差异! [root@www boot]# restore -C -f /root/boot.dump Dump date: Tue Dec 2 02:53:45 2008 Dumped from: the epoch Level 0 dump of /boot on www.vbird.tsai:/dev/hdc1 Label: /boot filesys = /boot restore: unable to stat ./config-2.6.18-128.el5: No such file or directory Some files were modified! 1 compare errors # 看到上面的特殊字体了吧!那就是有差异的部分!总共有一个文件被变更! # 我们刚刚确实有更动过该文件,嘿嘿!这样是否能了解?! # 2. 将文件系统改回来啊! [root@www boot]# mv config-2.6.18-128.el5-back config-2.6.18-128.el5 [root@www boot]# cd /root |
# 1. 先创建一个新的 partition 来使用,假设我们需要的是 150M 的容量 [root@www ~]# fdisk /dev/hdc Command (m for help): n First cylinder (2335-5005, default 2335): <==这里按 Enter Using default value 2335 Last cylinder or +size or +sizeM or +sizeK (2335-5005, default 5005): +150M Command (m for help): p ....中间省略.... /dev/hdc8 2335 2353 152586 83 Linux Command (m for help): w [root@www ~]# partprobe <==很重要的动作!别忘记! # 这样就能够创建一个 /dev/hdc8 的 partition ,然后继续格式化吧! [root@www ~]# mkfs -t ext3 /dev/hdc8 [root@www ~]# mount /dev/hdc8 /mnt # 2. 开始进行还原的动作!请您务必到新文件系统的挂载点底下去! [root@www ~]# cd /mnt [root@www mnt]# restore -r -f /root/boot.dump restore: ./lost+found: File exists |
仅还原部分文件的 restore 互动模式
[root@www ~]# cd /mnt [root@www mnt]# restore -i -f /root/etc.dump restore > # 此时你就已经进入 restore 的互动模式画面中!要注意的是: # 你目前已经在 etc.dump 这个文件内了!所有的动作都是在 etc.dump 内! restore > help Available commands are: ls [arg] - list directory <==列出 etc.dump 内的文件或目录 cd arg - change directory <==在 etc.dump 内变更目录 pwd - print current directory <==列出在 etc.dump 内的路径档名 add [arg] - add `arg' to list of files to be extracted delete [arg] - delete `arg' from list of files to be extracted extract - extract requested files # 上面三个命令是重点!各命令的功能为: # add file :将 file 加入等一下要解压缩的文件列表中 # delete file :将 file 移除出解压缩的列表,并非删除 etc.dump 内的文件!别误会!^_^ # extract :开始将刚刚选择的文件列表解压缩了去! setmodes - set modes of requested directories quit - immediately exit program what - list dump header information verbose - toggle verbose flag (useful with ``ls'') prompt - toggle the prompt display help or `?' - print this list restore > ls .: etc/ <==会显示出在 etc.dump 内主要的目录,因为我们备份 /etc ,所以档名为此! restore > cd etc <==在 etc.dump 内变换路径到 etc 目录下 restore > pwd <==列出本目录的档名为? /etc restore > ls passwd shadow group <==看看,真的有这三个文件喔! passwd shadow group restore > add passwd shadow group <==加入解压缩列表 restore > delete group <==加错了!将 group 移除解压缩列表 restore > ls passwd shadow group *passwd <==有要被解压缩的,档名之前会出现 * 的符号呢! *shadow group restore > extract <==开始进行解压缩去! You have not read any volumes yet. <==这里会询问你需要的volume Unless you know which volume your file(s) are on you should start with the last volume and work towards the first. Specify next volume # (none if no more volumes): 1 <==只有一个 volume set owner/mode for '.'? [yn] n <==不需要修改权限 restore > quit <==离开 restore 的功能 [root@www ~]# ll -d etc drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 1024 Dec 15 17:49 etc <==解压缩后,所创建出来的目录啦! [root@www ~]# ll etc total 6 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1945 Sep 29 02:21 passwd -r-------- 1 root root 1257 Sep 29 02:21 shadow |
A beautiful web dashboard for Linux
最近提交(Master分支:4 个月前 )
186a802e
added ecosystem file for PM2 5 年前
5def40a3
Add host customization support for the NodeJS version 5 年前

AtomGit 是由开放原子开源基金会联合 CSDN 等生态伙伴共同推出的新一代开源与人工智能协作平台。平台坚持“开放、中立、公益”的理念,把代码托管、模型共享、数据集托管、智能体开发体验和算力服务整合在一起,为开发者提供从开发、训练到部署的一站式体验。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容







所有评论(0)