Java多线程:ThreadPoolExecutor详解
ThreadPoolExecutor是JDK并发包提供的一个线程池服务,基于ThreadPoolExecutor可以很容易将一个Runnable接口的任务放入线程池中。
ThreadPoolExecutor的构建参数:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), handler);
}corePoolSize: 核心线程数,会一直存活,即使没有任务,线程池也会维护线程的最少数量
maximumPoolSize: 线程池维护线程的最大数量
keepAliveTime: 线程池维护线程所允许的空闲时间,当线程空闲时间达到keepAliveTime,该线程会退出,直到线程数量等于corePoolSize。如果allowCoreThreadTimeout设置为true,则所有线程均会退出直到线程数量为0。
unit: 线程池维护线程所允许的空闲时间的单位、可选参数值为:TimeUnit中的几个静态属性:NANOSECONDS、MICROSECONDS、MILLISECONDS、SECONDS。
workQueue: 线程池所使用的缓冲队列,常用的是:java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue、LinkedBlockingQueue、SynchronousQueue
handler: 线程池中的数量大于maximumPoolSize,对拒绝任务的处理策略,默认值ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()。
2. execute方法JDK 实现
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (poolSize >= corePoolSize || !addIfUnderCorePoolSize(command)) {
if (runState == RUNNING && workQueue.offer(command)) {
if (runState != RUNNING || poolSize == 0)
ensureQueuedTaskHandled(command);
}
else if (!addIfUnderMaximumPoolSize(command))
reject(command); // is shutdown or saturated
}
}一个任务通过 execute(Runnable)方法被添加到线程池,任务就是一个Runnable类型的对象,任务的执行方法就是run()方法,如果传入的为null,侧抛出NullPointerException。
如果当前线程数小于corePoolSize,调用addIfUnderCorePoolSize方法,addIfUnderCorePoolSize方法首先调用mainLock加锁,再次判断当前线程数小于corePoolSize并且线程池处于RUNNING状态,则调用addThread增加线程
addIfUnderCorePoolSize方法实现:
private boolean addIfUnderCorePoolSize(Runnable firstTask) {
Thread t = null;
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
if (poolSize < corePoolSize && runState == RUNNING)
t = addThread(firstTask);
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
if (t == null)
return false;
t.start();
return true;
}addThread方法实现:
private Thread addThread(Runnable firstTask) {
Worker w = new Worker(firstTask);
Thread t = threadFactory.newThread(w);
if (t != null) {
w.thread = t;
workers.add(w);
int nt = ++poolSize;
if (nt > largestPoolSize)
largestPoolSize = nt;
}
return t;
}ThreadFactory 接口默认实现DefaultThreadFactory
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(group, r,
namePrefix + threadNumber.getAndIncrement(),
0);
if (t.isDaemon())
t.setDaemon(false);
if (t.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY)
t.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
return t;
}从addThread方法看得出,Worker对象包装了参数传入的任务,threadFactory新创建的线程包装了Worker对象,在执行新创建线程的run方法时,调用到了Worker对象的run方法.
Worker的run方法
public void run() {
try {
Runnable task = firstTask;
firstTask = null;
while (task != null || (task = getTask()) != null) {
runTask(task);
task = null;
}
} finally {
workerDone(this);
}
}从以上方法可以看出,Worker所在的线程启动后,首先执行创建其时传入的Runnable任务,执行完成后,循环调用getTask来获取新的任务,在没有任务的情况下,退出此线程。
getTask方法实现:
Runnable getTask() {
for (;;) {
try {
int state = runState;
if (state > SHUTDOWN)
return null;
Runnable r;
if (state == SHUTDOWN) // Help drain queue
r = workQueue.poll();
else if (poolSize > corePoolSize || allowCoreThreadTimeOut)
r = workQueue.poll(keepAliveTime, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
else
r = workQueue.take();
if (r != null)
return r;
if (workerCanExit()) {
if (runState >= SHUTDOWN) // Wake up others
interruptIdleWorkers();
return null;
}
// Else retry
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
// On interruption, re-check runState
}
}
}回到execute方法 ,execute 方法部分实现:
if (runState == RUNNING && workQueue.offer(command)) {
if (runState != RUNNING || poolSize == 0)
ensureQueuedTaskHandled(command);
}
else if (!addIfUnderMaximumPoolSize(command))
reject(command); // is shutdown or saturated如果当前线程池数量大于corePoolSize或addIfUnderCorePoolSize方法执行失败,则执行后续操作;如果线程池处于运行状态并且workQueue中成功加入任务,再次判断如果线程池的状态不为运行状态或当前线程池数为0,则调用ensureQueuedTaskHandled方法
ensureQueuedTaskHandled方法实现:
private void ensureQueuedTaskHandled(Runnable command) {
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
boolean reject = false;
Thread t = null;
try {
int state = runState;
if (state != RUNNING && workQueue.remove(command))
reject = true;
else if (state < STOP &&
poolSize < Math.max(corePoolSize, 1) &&
!workQueue.isEmpty())
t = addThread(null);
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
if (reject)
reject(command);
else if (t != null)
t.start();
}reject方法实现:
void reject(Runnable command) {
handler.rejectedExecution(command, this);
}
再次回到execute方法,
if (runState == RUNNING && workQueue.offer(command)) {
if (runState != RUNNING || poolSize == 0)
ensureQueuedTaskHandled(command);
}
else if (!addIfUnderMaximumPoolSize(command))
reject(command); // is shutdown or saturated
private boolean addIfUnderMaximumPoolSize(Runnable firstTask) {
Thread t = null;
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
if (poolSize < maximumPoolSize && runState == RUNNING)
t = addThread(firstTask);
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
if (t == null)
return false;
t.start();
return true;
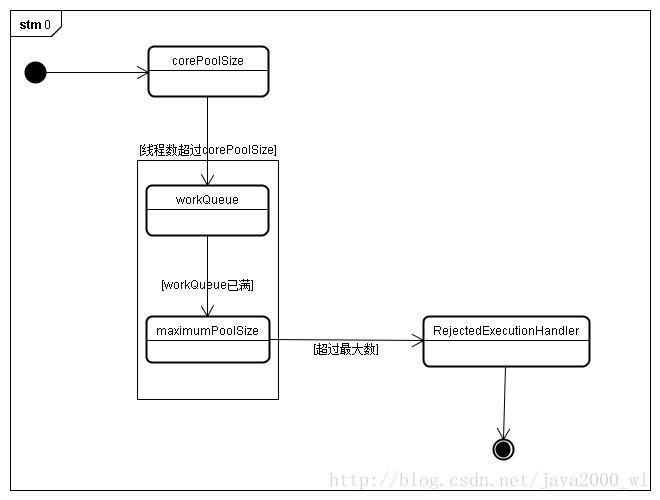
}3. 添加任务处理流程
当一个任务通过execute(Runnable)方法欲添加到线程池时:
如果当前线程池中的数量小于corePoolSize,并线程池处于Running状态,创建并添加的任务。
如果当前线程池中的数量等于corePoolSize,并线程池处于Running状态,缓冲队列 workQueue未满,那么任务被放入缓冲队列、等待任务调度执行。
如果当前线程池中的数量大于corePoolSize,缓冲队列workQueue已满,并且线程池中的数量小于maximumPoolSize,新提交任务会创建新线程执行任务。
如果当前线程池中的数量大于corePoolSize,缓冲队列workQueue已满,并且线程池中的数量等于maximumPoolSize,新提交任务由Handler处理。
当线程池中的线程大于corePoolSize时,多余线程空闲时间超过keepAliveTime时,会关闭这部分线程。
4. RejectedExecutionHandler 默认有四个选择:
ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy() 当线程池中的数量等于最大线程数时、直接抛出抛出java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException异常
public static class AbortPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates an {@code AbortPolicy}.
*/
public AbortPolicy() { }
/**
* Always throws RejectedExecutionException.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
* @throws RejectedExecutionException always.
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
throw new RejectedExecutionException("Task " + r.toString() +
" rejected from " +
e.toString());
}
}ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy() 当线程池中的数量等于最大线程数时、重试执行当前的任务,交由调用者线程来执行任务
public static class CallerRunsPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates a {@code CallerRunsPolicy}.
*/
public CallerRunsPolicy() { }
/**
* Executes task r in the caller's thread, unless the executor
* has been shut down, in which case the task is discarded.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
if (!e.isShutdown()) {
r.run();
}
}
}ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy() 当线程池中的数量等于最大线程数时、抛弃线程池中最后一个要执行的任务,并执行新传入的任务
public static class DiscardOldestPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates a {@code DiscardOldestPolicy} for the given executor.
*/
public DiscardOldestPolicy() { }
/**
* Obtains and ignores the next task that the executor
* would otherwise execute, if one is immediately available,
* and then retries execution of task r, unless the executor
* is shut down, in which case task r is instead discarded.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
if (!e.isShutdown()) {
e.getQueue().poll();
e.execute(r);
}
}
} public static class DiscardPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates a {@code DiscardPolicy}.
*/
public DiscardPolicy() { }
/**
* Does nothing, which has the effect of discarding task r.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
}
}更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容







所有评论(0)