数据集制作(YOLOv3)【附Labelimg下载链接】
Labelimage下载链接:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1bo6ItfZBc1DAbrt384m52w
提取码:sdp8
- labelimg简介
LabelImg 是一个图形图像注释工具,采用 Python 编写而成,并使用 Qt 作为其图形界面。 - 数据标注
运用Labelimg工具,创建所需要的类别,并进行标注处理
- 创建类别
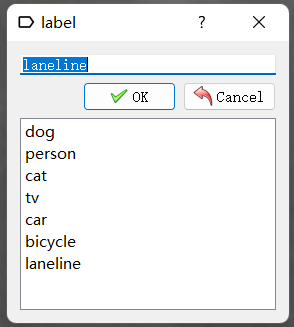
- 标注数据

- labelimag相关说明及快捷键
“Open”是打开单个图像
“Open Dir” 打开文件夹
“Change Save Dir” 图像保存的路径
“Next Image” 切换到下一张图像
“Prev Image”切换到上一张图像
“Verify Image”校验图像
“Save”保存图像
“Create RectBox”画标注框一个
“Duplicate RectBox”重复标注框
“Delete RectBox”删除标注框
“Zoom In”放大图像
“Zoom Out” 缩小图像
“Fit Window”图像适用窗口
“Fit Width”图像适应宽度。
| 快捷按键 | 对应功能 |
|---|---|
| Ctrl + u | 加载目录中的所有图像,鼠标点击Open dir同功能 |
| Ctrl + r | 更改默认注释目标目录(xml文件保存的地址) |
| Ctrl + s | 保存 |
| Ctrl + d | 复制当前标签和矩形框 |
| space | 将当前图像标记为已验证 |
| Ctrl++ | 放大 |
| Ctrl+ - | 缩小 |
-
xml文件转换
xml 文件信息中的 object 就表示标注的目标,在这里也就是图片中的车道线;name表示标注目标的类别;bndbox 就表示这个目标在图像中的位置,以图像左上顶点分别向右和向下建立 xy 坐标系,那么 xmin,ymin就表示矩形框左上顶点的横、纵坐标,同理,xmax,ymax 就表示矩形框右下顶点的横、纵坐标,通过这四个坐标就可以知道车辆在图像中的位置信息
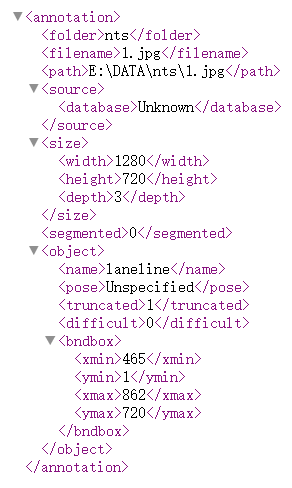
txt标签数据中,每一行中 0 就代表标注目标的类别,因为类别是从 0 开始,我们只有一个类别 laneline,所以第一个数字就为 0。后面的数字依次分别代表归一化中心横坐标(x_center),归一化中心纵坐标(y_center),以及归一化宽度w和归一化高度h,通过这四个坐标也可以得到车辆在图像中的位置信息,与 xml 文件中坐标表示的位置信息是一致的。
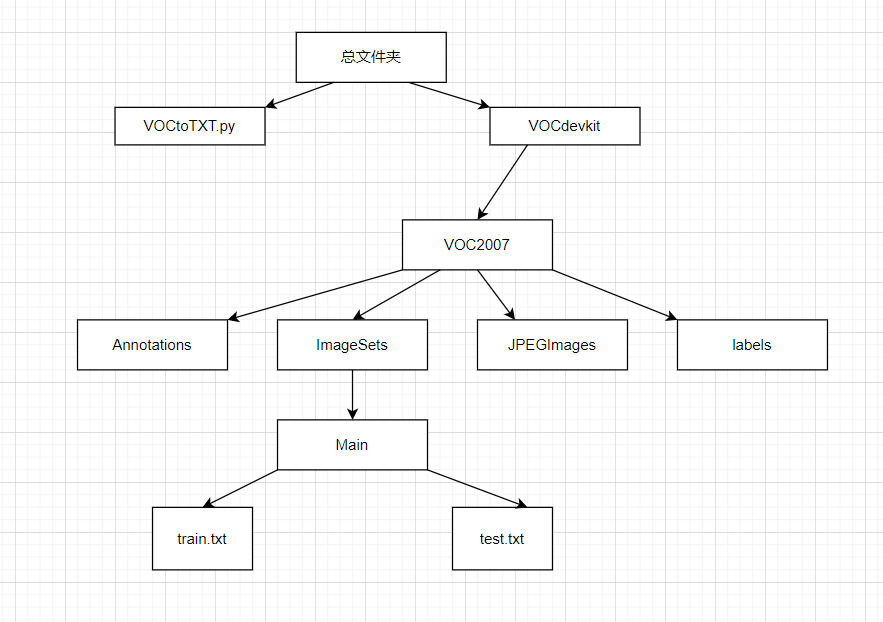
新建文件夹,文件结构如下:
- 转换代码VOCtoTXT.py:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import pickle
import os
from os import listdir, getcwd
from os.path import join
import random
classes=["A"]
def clear_hidden_files(path):
dir_list = os.listdir(path)
for i in dir_list:
abspath = os.path.join(os.path.abspath(path), i)
if os.path.isfile(abspath):
if i.startswith("._"):
os.remove(abspath)
else:
clear_hidden_files(abspath)
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1./size[0]
dh = 1./size[1]
x = (box[0] + box[1])/2.0
y = (box[2] + box[3])/2.0
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x*dw
w = w*dw
y = y*dh
h = h*dh
return (x,y,w,h)
def convert_annotation(image_id):
in_file = open('VOCdevkit\VOC2007\Annotations\%s.xml' %image_id,'r',encoding='UTF-8')
out_file = open('VOCdevkit\VOC2007\labels\%s.txt' %image_id, 'w')
tree=ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
if size==None:
print("image_id =%s\n" %image_id)
return
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
bb = convert((w,h), b)
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
in_file.close()
out_file.close()
wd = os.getcwd()
wd = os.getcwd()
work_sapce_dir = os.path.join(wd, "VOCdevkit\\")
if not os.path.isdir(work_sapce_dir):
os.mkdir(work_sapce_dir)
work_sapce_dir = os.path.join(work_sapce_dir, "VOC2007\\")
if not os.path.isdir(work_sapce_dir):
os.mkdir(work_sapce_dir)
annotation_dir = os.path.join(work_sapce_dir, "Annotations\\")
if not os.path.isdir(annotation_dir):
os.mkdir(annotation_dir)
clear_hidden_files(annotation_dir)
image_dir = os.path.join(work_sapce_dir, "JPEGImages\\")
if not os.path.isdir(image_dir):
os.mkdir(image_dir)
clear_hidden_files(image_dir)
VOC_file_dir = os.path.join(work_sapce_dir, "ImageSets\\")
if not os.path.isdir(VOC_file_dir):
os.mkdir(VOC_file_dir)
VOC_file_dir = os.path.join(VOC_file_dir, "Main\\")
if not os.path.isdir(VOC_file_dir):
os.mkdir(VOC_file_dir)
train_file = open(os.path.join(wd, "2007_train.txt"), 'w')
test_file = open(os.path.join(wd, "2007_test.txt"), 'w')
train_file.close()
test_file.close()
VOC_train_file = open(os.path.join(work_sapce_dir, "ImageSets\\Main\\train.txt"), 'w')
VOC_test_file = open(os.path.join(work_sapce_dir, "ImageSets\\Main\\test.txt"), 'w')
VOC_train_file.close()
VOC_test_file.close()
if not os.path.exists('VOCdevkit\\VOC2007\\labels'):
os.makedirs('VOCdevkit\\VOC2007\\labels')
train_file = open(os.path.join(wd, "2007_train.txt"), 'a')
test_file = open(os.path.join(wd, "2007_test.txt"), 'a')
VOC_train_file = open(os.path.join(work_sapce_dir, "ImageSets\\Main\\train.txt"), 'a')
VOC_test_file = open(os.path.join(work_sapce_dir, "ImageSets\\Main\\test.txt"), 'a')
list = os.listdir(image_dir) # list image files
probo = random.randint(1, 100)
print("Probobility: %d" % probo)
for i in range(0,len(list)):
path = os.path.join(image_dir,list[i])
if os.path.isfile(path):
image_path = image_dir + list[i]
voc_path = list[i]
(nameWithoutExtention, extention) = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(image_path))
(voc_nameWithoutExtention, voc_extention) = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(voc_path))
annotation_name = nameWithoutExtention + '.xml'
annotation_path = os.path.join(annotation_dir, annotation_name)
probo = random.randint(1, 100)
print("Probobility: %d" % probo)
if(probo < 80):
if os.path.exists(annotation_path):
train_file.write(image_path + '\n')
VOC_train_file.write(voc_nameWithoutExtention + '\n')
convert_annotation(nameWithoutExtention)
else:
if os.path.exists(annotation_path):
test_file.write(image_path + '\n')
VOC_test_file.write(voc_nameWithoutExtention + '\n')
convert_annotation(nameWithoutExtention)
train_file.close()
test_file.close()
VOC_train_file.close()
VOC_test_file.close()

Annotations用来存放xml格式的标注文件;
ImageSets该文件夹里原有三个子文件夹,但实验中我们仅需要使用Main文件夹里面的信息,存放的是图像物体识别的数据,有train.txt, test.txt 文件,这几个文件我们后面会生成。
JPEGImages存放图片数据集;
labels存放转换后的txt标注文件,目前是空文件夹。
完成上述步骤之后数据集训练完成
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容









所有评论(0)