OpenMMlab导出yolox模型并用onnxruntime和tensorrt推理
onnxruntime
microsoft/onnxruntime: 是一个用于运行各种机器学习模型的开源库。适合对机器学习和深度学习有兴趣的人,特别是在开发和部署机器学习模型时需要处理各种不同框架和算子的人。特点是支持多种机器学习框架和算子,包括 TensorFlow、PyTorch、Caffe 等,具有高性能和广泛的兼容性。
项目地址:https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/on/onnxruntime
·
导出onnx文件
直接使用脚本
import torch
from mmdet.apis import init_detector, inference_detector
config_file = './configs/yolox/yolox_tiny_8xb8-300e_coco.py'
checkpoint_file = 'yolox_tiny_8x8_300e_coco_20211124_171234-b4047906.pth'
model = init_detector(config_file, checkpoint_file, device='cpu') # or device='cuda:0'
torch.onnx.export(model, (torch.zeros(1, 3, 416, 416),), "yolox.onnx", opset_version=11)
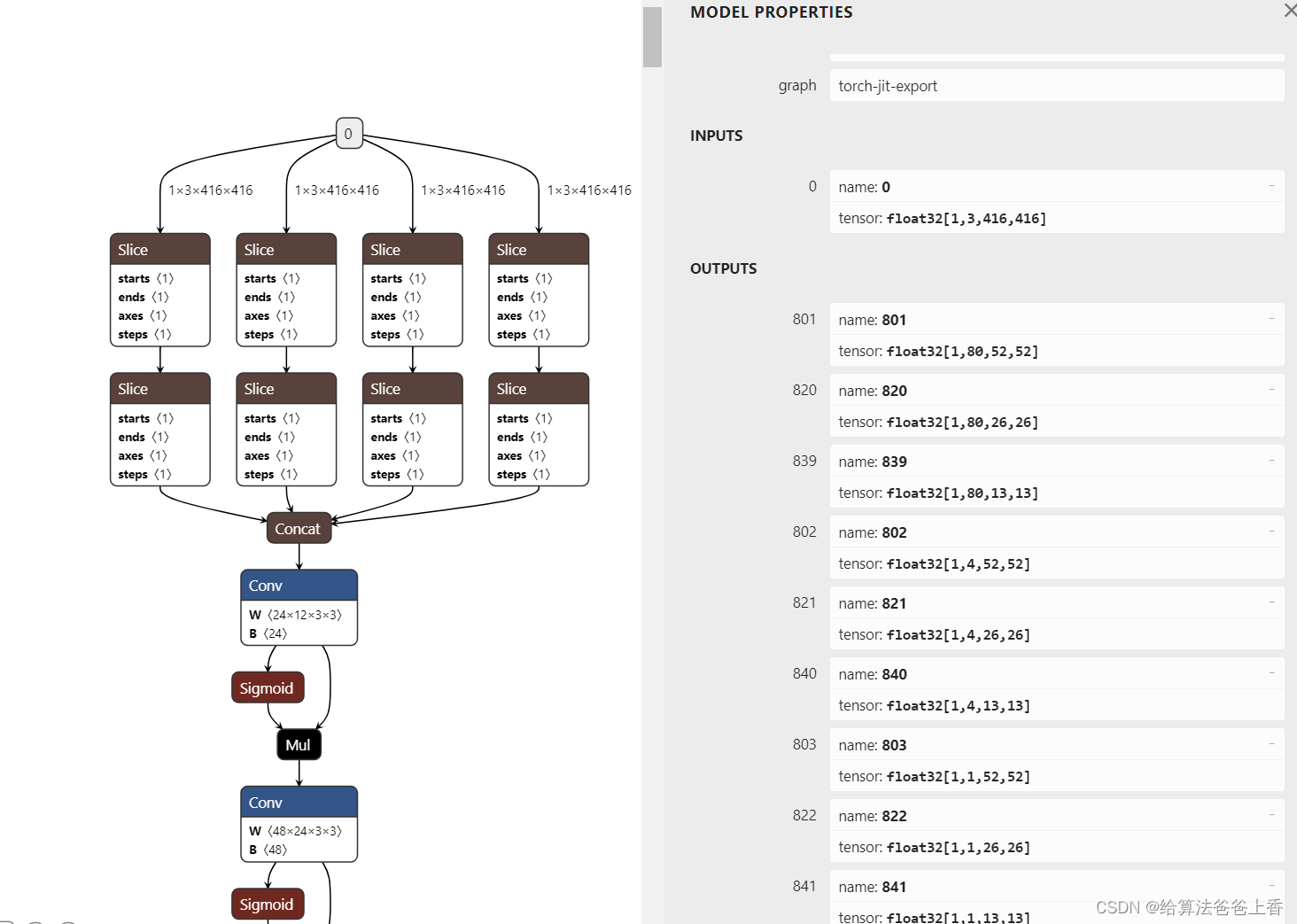
导出的onnx结构如下:

输出是包含多个检测头的输出。若需要合并检测结果,需要修改脚本如下:
import torch
import cv2
import numpy as np
from mmdet.apis import init_detector, inference_detector
config_file = './configs/yolox/yolox_tiny_8xb8-300e_coco.py'
checkpoint_file = 'yolox_tiny_8x8_300e_coco_20211124_171234-b4047906.pth'
model = init_detector(config_file, checkpoint_file, device='cpu') # or device='cuda:0'
class YOLOX(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.model = init_detector(config_file, checkpoint_file, device='cpu')
self.class_num = 80
self.strides = [(8, 8), (16, 16), (32, 32)]
def _meshgrid(self, x, y):
yy, xx = torch.meshgrid(y, x)
return xx.reshape(-1), yy.reshape(-1)
def grid_priors(self, featmap_sizes):
multi_level_priors = []
for i in range(len(featmap_sizes)):
feat_h, feat_w = featmap_sizes[i]
stride_w, stride_h = self.strides[i]
shift_x = torch.arange(0, feat_w) * stride_w
shift_y = torch.arange(0, feat_h) * stride_h
shift_xx, shift_yy = self._meshgrid(shift_x, shift_y)
stride_w = shift_xx.new_full((shift_xx.shape[0], ), stride_w)
stride_h = shift_xx.new_full((shift_yy.shape[0], ), stride_h)
shifts = torch.stack([shift_xx, shift_yy, stride_w, stride_h], dim=-1)
multi_level_priors.append(shifts)
return multi_level_priors
def bbox_decode(self, priors, bbox_preds):
xys = (bbox_preds[..., :2] * priors[:, 2:]) + priors[:, :2]
whs = bbox_preds[..., 2:].exp() * priors[:, 2:]
tl_x = (xys[..., 0] - whs[..., 0] / 2)
tl_y = (xys[..., 1] - whs[..., 1] / 2)
br_x = (xys[..., 0] + whs[..., 0] / 2)
br_y = (xys[..., 1] + whs[..., 1] / 2)
decoded_bboxes = torch.stack([tl_x, tl_y, br_x, br_y], -1)
return decoded_bboxes
def forward(self, x):
x = self.model.backbone(x)
x = self.model.neck(x)
pred_maps = self.model.bbox_head(x)
cls_scores, bbox_preds, objectnesses = pred_maps
featmap_sizes = [cls_score.shape[2:] for cls_score in cls_scores]
mlvl_priors = self.grid_priors(featmap_sizes)
flatten_cls_scores = [cls_score.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).reshape(1, -1, self.class_num) for cls_score in cls_scores]
flatten_bbox_preds = [bbox_pred.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).reshape(1, -1, 4) for bbox_pred in bbox_preds]
flatten_objectness = [objectness.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).reshape(1, -1) for objectness in objectnesses]
flatten_cls_scores = torch.cat(flatten_cls_scores, dim=1).sigmoid()
flatten_bbox_preds = torch.cat(flatten_bbox_preds, dim=1)
flatten_objectness = torch.cat(flatten_objectness, dim=1).sigmoid()
flatten_priors = torch.cat(mlvl_priors)
flatten_bboxes = self.bbox_decode(flatten_priors, flatten_bbox_preds)
return flatten_bboxes, flatten_objectness, flatten_cls_scores
model = YOLOX().eval()
input = torch.zeros(1, 3, 416, 416, device='cpu')
torch.onnx.export(model, input, "yolox.onnx", opset_version=11)
导出的onnx结构如下:

安装mmdeploy的话,可以通过下面脚本导出onnx模型。
from mmdeploy.apis import torch2onnx
from mmdeploy.backend.sdk.export_info import export2SDK
img = 'bus.jpg'
work_dir = './work_dir/onnx/yolox'
save_file = './end2end.onnx'
deploy_cfg = 'mmdeploy/configs/mmdet/detection/detection_onnxruntime_dynamic.py'
model_cfg = 'mmdetection/configs/yolox/yolox_tiny_8xb8-300e_coco.py'
model_checkpoint = 'checkpoints/yolox_tiny_8x8_300e_coco_20211124_171234-b4047906.pth'
device = 'cpu'
# 1. convert model to onnx
torch2onnx(img, work_dir, save_file, deploy_cfg, model_cfg, model_checkpoint, device)
# 2. extract pipeline info for sdk use (dump-info)
export2SDK(deploy_cfg, model_cfg, work_dir, pth=model_checkpoint, device=device)
onnx模型的结构如下:
onnxruntime推理
手动导出的onnx模型使用onnxruntime推理:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import onnxruntime
class_names = ['person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus', 'train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light',
'fire hydrant', 'stop sign', 'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse', 'sheep', 'cow',
'elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'backpack', 'umbrella', 'handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee',
'skis', 'snowboard', 'sports ball', 'kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove', 'skateboard', 'surfboard',
'tennis racket', 'bottle', 'wine glass', 'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl', 'banana', 'apple',
'sandwich', 'orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza', 'donut', 'cake', 'chair', 'couch',
'potted plant', 'bed', 'dining table', 'toilet', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard', 'cell phone',
'microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink', 'refrigerator', 'book', 'clock', 'vase', 'scissors', 'teddy bear',
'hair drier', 'toothbrush'] #coco80类别
input_shape = (416, 416)
score_threshold = 0.2
nms_threshold = 0.5
confidence_threshold = 0.2
def nms(boxes, scores, score_threshold, nms_threshold):
x1 = boxes[:, 0]
y1 = boxes[:, 1]
x2 = boxes[:, 2]
y2 = boxes[:, 3]
areas = (y2 - y1 + 1) * (x2 - x1 + 1)
keep = []
index = scores.argsort()[::-1]
while index.size > 0:
i = index[0]
keep.append(i)
x11 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[index[1:]])
y11 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[index[1:]])
x22 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[index[1:]])
y22 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[index[1:]])
w = np.maximum(0, x22 - x11 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0, y22 - y11 + 1)
overlaps = w * h
ious = overlaps / (areas[i] + areas[index[1:]] - overlaps)
idx = np.where(ious <= nms_threshold)[0]
index = index[idx + 1]
return keep
def filter_box(outputs):
outputs0, outputs1, outputs2 = outputs
flag = outputs1 > confidence_threshold
output0 = outputs0[flag].reshape(-1, 4)
output1 = outputs1[flag].reshape(-1, 1)
classes_scores = outputs2[flag].reshape(-1, 80)
outputs = np.concatenate((output0, output1, classes_scores), axis=1)
boxes = []
scores = []
class_ids = []
for i in range(len(classes_scores)):
class_id = np.argmax(classes_scores[i])
outputs[i][4] *= classes_scores[i][class_id]
outputs[i][5] = class_id
if outputs[i][4] > score_threshold:
boxes.append(outputs[i][:6])
scores.append(outputs[i][4])
class_ids.append(outputs[i][5])
boxes = np.array(boxes)
scores = np.array(scores)
indices = nms(boxes, scores, score_threshold, nms_threshold)
output = boxes[indices]
return output
def letterbox(im, new_shape=(416, 416), color=(114, 114, 114)):
# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
shape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
# Compute padding
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = (new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0])/2, (new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1])/2 # wh padding
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return im
def scale_boxes(boxes, shape):
# Rescale boxes (xyxy) from input_shape to shape
gain = min(input_shape[0] / shape[0], input_shape[1] / shape[1]) # gain = old / new
pad = (input_shape[1] - shape[1] * gain) / 2, (input_shape[0] - shape[0] * gain) / 2 # wh padding
boxes[..., [0, 2]] -= pad[0] # x padding
boxes[..., [1, 3]] -= pad[1] # y padding
boxes[..., :4] /= gain
boxes[..., [0, 2]] = boxes[..., [0, 2]].clip(0, shape[1]) # x1, x2
boxes[..., [1, 3]] = boxes[..., [1, 3]].clip(0, shape[0]) # y1, y2
return boxes
def draw(image, box_data):
box_data = scale_boxes(box_data, image.shape)
boxes = box_data[...,:4].astype(np.int32)
scores = box_data[...,4]
classes = box_data[...,5].astype(np.int32)
for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):
top, left, right, bottom = box
cv2.rectangle(image, (top, left), (right, bottom), (255, 0, 0), 1)
cv2.putText(image, '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(class_names[cl], score), (top, left), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 0, 255), 1)
if __name__=="__main__":
image = cv2.imread('bus.jpg')
input = letterbox(image, input_shape)
input = cv2.resize(image, input_shape)
input = input[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1).astype(dtype=np.float32) #BGR2RGB和HWC2CHW
input = np.expand_dims(input, axis=0)
onnx_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession('yolox.onnx', providers=['CPUExecutionProvider'])
input_name = []
for node in onnx_session.get_inputs():
input_name.append(node.name)
output_name = []
for node in onnx_session.get_outputs():
output_name.append(node.name)
inputs = {}
for name in input_name:
inputs[name] = input
outputs = onnx_session.run(None, inputs)
boxes = filter_box(outputs)
draw(image, boxes)
cv2.imwrite('result.jpg', image)
mmdeploy导出的onnx模型使用onnxruntime推理:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import onnxruntime
class_names = ['person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus', 'train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light',
'fire hydrant', 'stop sign', 'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse', 'sheep', 'cow',
'elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'backpack', 'umbrella', 'handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee',
'skis', 'snowboard', 'sports ball', 'kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove', 'skateboard', 'surfboard',
'tennis racket', 'bottle', 'wine glass', 'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl', 'banana', 'apple',
'sandwich', 'orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza', 'donut', 'cake', 'chair', 'couch',
'potted plant', 'bed', 'dining table', 'toilet', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard', 'cell phone',
'microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink', 'refrigerator', 'book', 'clock', 'vase', 'scissors', 'teddy bear',
'hair drier', 'toothbrush'] #coco80类别
input_shape = (416, 416)
confidence_threshold = 0.2
def filter_box(outputs): #删除置信度小于confidence_threshold的BOX
flag = outputs[0][..., 4] > confidence_threshold
boxes = outputs[0][flag]
class_ids = outputs[1][flag].reshape(-1, 1)
output = np.concatenate((boxes, class_ids), axis=1)
return output
def letterbox(im, new_shape=(416, 416), color=(114, 114, 114)):
# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
shape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
# Compute padding
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = (new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0])/2, (new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1])/2 # wh padding
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return im
def scale_boxes(input_shape, boxes, shape):
# Rescale boxes (xyxy) from input_shape to shape
gain = min(input_shape[0] / shape[0], input_shape[1] / shape[1]) # gain = old / new
pad = (input_shape[1] - shape[1] * gain) / 2, (input_shape[0] - shape[0] * gain) / 2 # wh padding
boxes[..., [0, 2]] -= pad[0] # x padding
boxes[..., [1, 3]] -= pad[1] # y padding
boxes[..., :4] /= gain
boxes[..., [0, 2]] = boxes[..., [0, 2]].clip(0, shape[1]) # x1, x2
boxes[..., [1, 3]] = boxes[..., [1, 3]].clip(0, shape[0]) # y1, y2
return boxes
def draw(image, box_data):
box_data = scale_boxes(input_shape, box_data, image.shape)
boxes = box_data[...,:4].astype(np.int32)
scores = box_data[...,4]
classes = box_data[...,5].astype(np.int32)
for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):
top, left, right, bottom = box
cv2.rectangle(image, (top, left), (right, bottom), (255, 0, 0), 1)
cv2.putText(image, '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(class_names[cl], score), (top, left), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 0, 255), 1)
if __name__=="__main__":
image = cv2.imread('bus.jpg')
input = letterbox(images, input_shape)
input = input[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1).astype(dtype=np.float32) #BGR2RGB和HWC2CHW
input = np.expand_dims(input, axis=0)
onnx_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession('../work_dir/onnx/yolox/end2end.onnx', providers=['CPUExecutionProvider'])
input_name = []
for node in onnx_session.get_inputs():
input_name.append(node.name)
output_name = []
for node in onnx_session.get_outputs():
output_name.append(node.name)
inputs = {}
for name in input_name:
inputs[name] = input
outputs = onnx_session.run(None, inputs)
boxes = filter_box(outputs)
draw(image, boxes)
cv2.imwrite('result.jpg', image)
直接使用mmdeploy的api推理:
from mmdeploy.apis import inference_model
model_cfg = 'mmdetection/configs/yolox/yolox_tiny_8xb8-300e_coco.py'
deploy_cfg = 'mmdeploy/configs/mmdet/detection/detection_onnxruntime_dynamic.py'
img = 'bus.jpg'
backend_files = ['work_dir/onnx/yolox/end2end.onnx']
device = 'cpu'
result = inference_model(model_cfg, deploy_cfg, backend_files, img, device)
print(result)
或者:
from mmdeploy_runtime import Detector
import cv2
# 读取图片
img = cv2.imread('bus.jpg')
# 创建检测器
detector = Detector(model_path='work_dir/onnx/yolox', device_name='cpu')
# 执行推理
bboxes, labels, _ = detector(img)
# 使用阈值过滤推理结果,并绘制到原图中
indices = [i for i in range(len(bboxes))]
for index, bbox, label_id in zip(indices, bboxes, labels):
[left, top, right, bottom], score = bbox[0:4].astype(int), bbox[4]
if score < 0.3:
continue
cv2.rectangle(img, (left, top), (right, bottom), (0, 255, 0))
cv2.imwrite('result.jpg', img)
导出engine文件
方法一:通过trtexec转换onnx文件,LZ的版本是TensorRT-8.2.1.8。
./trtexec.exe --onnx=yolox.onnx --saveEngine=yolox.engine --workspace=20480
方法二:通过mmdeploy导出engine文件。
from mmdeploy.apis import torch2onnx
from mmdeploy.backend.tensorrt.onnx2tensorrt import onnx2tensorrt
from mmdeploy.backend.sdk.export_info import export2SDK
import os
img = 'demo.JPEG'
work_dir = './work_dir/trt/yolox'
save_file = './end2end.onnx'
deploy_cfg = 'mmdeploy/configs/mmdet/detection/detection_tensorrt_static-320x320.py'
model_cfg = 'mmdetection/configs/yolox/yolox_tiny_8xb8-300e_coco.py'
model_checkpoint = 'checkpoints/yolox_tiny_8x8_300e_coco_20211124_171234-b4047906.pth'
device = 'cuda'
# 1. convert model to IR(onnx)
torch2onnx(img, work_dir, save_file, deploy_cfg, model_cfg, model_checkpoint, device)
# 2. convert IR to tensorrt
onnx_model = os.path.join(work_dir, save_file)
save_file = 'end2end.engine'
model_id = 0
device = 'cuda'
onnx2tensorrt(work_dir, save_file, model_id, deploy_cfg, onnx_model, device)
# 3. extract pipeline info for sdk use (dump-info)
export2SDK(deploy_cfg, model_cfg, work_dir, pth=model_checkpoint, device=device)
tensorrt推理
手动导出的模型使用tensorrt推理:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import tensorrt as trt
import pycuda.autoinit
import pycuda.driver as cuda
class_names = ['person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus', 'train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light',
'fire hydrant', 'stop sign', 'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse', 'sheep', 'cow',
'elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'backpack', 'umbrella', 'handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee',
'skis', 'snowboard', 'sports ball', 'kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove', 'skateboard', 'surfboard',
'tennis racket', 'bottle', 'wine glass', 'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl', 'banana', 'apple',
'sandwich', 'orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza', 'donut', 'cake', 'chair', 'couch',
'potted plant', 'bed', 'dining table', 'toilet', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard', 'cell phone',
'microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink', 'refrigerator', 'book', 'clock', 'vase', 'scissors', 'teddy bear',
'hair drier', 'toothbrush'] #coco80类别
input_shape = (416, 416)
score_threshold = 0.2
nms_threshold = 0.5
confidence_threshold = 0.2
def nms(boxes, scores, score_threshold, nms_threshold):
x1 = boxes[:, 0]
y1 = boxes[:, 1]
x2 = boxes[:, 2]
y2 = boxes[:, 3]
areas = (y2 - y1 + 1) * (x2 - x1 + 1)
keep = []
index = scores.argsort()[::-1]
while index.size > 0:
i = index[0]
keep.append(i)
x11 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[index[1:]])
y11 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[index[1:]])
x22 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[index[1:]])
y22 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[index[1:]])
w = np.maximum(0, x22 - x11 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0, y22 - y11 + 1)
overlaps = w * h
ious = overlaps / (areas[i] + areas[index[1:]] - overlaps)
idx = np.where(ious <= nms_threshold)[0]
index = index[idx + 1]
return keep
def filter_box(outputs):
outputs0, outputs1, outputs2 = outputs
flag = outputs1 > confidence_threshold
output0 = outputs0[flag].reshape(-1, 4)
output1 = outputs1[flag].reshape(-1, 1)
classes_scores = outputs2[flag].reshape(-1, 80)
outputs = np.concatenate((output0, output1, classes_scores), axis=1)
boxes = []
scores = []
class_ids = []
for i in range(len(classes_scores)):
class_id = np.argmax(classes_scores[i])
outputs[i][4] *= classes_scores[i][class_id]
outputs[i][5] = class_id
if outputs[i][4] > score_threshold:
boxes.append(outputs[i][:6])
scores.append(outputs[i][4])
class_ids.append(outputs[i][5])
boxes = np.array(boxes)
scores = np.array(scores)
indices = nms(boxes, scores, score_threshold, nms_threshold)
output = boxes[indices]
return output
def letterbox(im, new_shape=(416, 416), color=(114, 114, 114)):
# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
shape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
# Compute padding
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = (new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0])/2, (new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1])/2 # wh padding
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return im
def scale_boxes(boxes, shape):
# Rescale boxes (xyxy) from input_shape to shape
gain = min(input_shape[0] / shape[0], input_shape[1] / shape[1]) # gain = old / new
pad = (input_shape[1] - shape[1] * gain) / 2, (input_shape[0] - shape[0] * gain) / 2 # wh padding
boxes[..., [0, 2]] -= pad[0] # x padding
boxes[..., [1, 3]] -= pad[1] # y padding
boxes[..., :4] /= gain
boxes[..., [0, 2]] = boxes[..., [0, 2]].clip(0, shape[1]) # x1, x2
boxes[..., [1, 3]] = boxes[..., [1, 3]].clip(0, shape[0]) # y1, y2
return boxes
def draw(image, box_data):
box_data = scale_boxes(box_data, image.shape)
boxes = box_data[...,:4].astype(np.int32)
scores = box_data[...,4]
classes = box_data[...,5].astype(np.int32)
for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):
top, left, right, bottom = box
cv2.rectangle(image, (top, left), (right, bottom), (255, 0, 0), 1)
cv2.putText(image, '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(class_names[cl], score), (top, left), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 0, 255), 1)
if __name__=="__main__":
logger = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.WARNING)
with open("yolox.engine", "rb") as f, trt.Runtime(logger) as runtime:
engine = runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read())
context = engine.create_execution_context()
h_input = cuda.pagelocked_empty(trt.volume(context.get_binding_shape(0)), dtype=np.float32)
h_output0 = cuda.pagelocked_empty(trt.volume(context.get_binding_shape(1)), dtype=np.float32)
h_output1 = cuda.pagelocked_empty(trt.volume(context.get_binding_shape(2)), dtype=np.float32)
h_output2 = cuda.pagelocked_empty(trt.volume(context.get_binding_shape(3)), dtype=np.float32)
d_input = cuda.mem_alloc(h_input.nbytes)
d_output0 = cuda.mem_alloc(h_output0.nbytes)
d_output1 = cuda.mem_alloc(h_output1.nbytes)
d_output2 = cuda.mem_alloc(h_output2.nbytes)
stream = cuda.Stream()
image = cv2.imread('bus.jpg')
input = letterbox(image, input_shape)
input = input[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1).astype(dtype=np.float32) #BGR2RGB和HWC2CHW
input = np.expand_dims(input, axis=0)
np.copyto(h_input, input.ravel())
with engine.create_execution_context() as context:
cuda.memcpy_htod_async(d_input, h_input, stream)
context.execute_async_v2(bindings=[int(d_input), int(d_output0), int(d_output1), int(d_output2)], stream_handle=stream.handle)
cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(h_output0, d_output0, stream)
cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(h_output1, d_output1, stream)
cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(h_output2, d_output2, stream)
stream.synchronize()
h_output = []
h_output.append(h_output2.reshape(1, 3549, 4))
h_output.append(h_output1.reshape(1, 3549))
h_output.append(h_output0.reshape(1, 3549, 80))
boxes = filter_box(h_output)
draw(image, boxes)
cv2.imwrite('result.jpg', image)
使用mmdeploy的api推理:
from mmdeploy.apis import inference_model
model_cfg = 'mmdetection/configs/yolox/yolox_tiny_8xb8-300e_coco.py'
deploy_cfg = 'mmdeploy/configs/mmdet/detection/detection_tensorrt_static-320x320.py'
img = 'mmdetection/demo/demo.jpg'
backend_files = ['work_dir/trt/yolox/end2end.engine']
device = 'cuda'
result = inference_model(model_cfg, deploy_cfg, backend_files, img, device)
print(result)
或者
from mmdeploy_runtime import Detector
import cv2
# 读取图片
img = cv2.imread('bus.jpg')
# 创建检测器
detector = Detector(model_path='work_dir/trt/yolox', device_name='cuda')
# 执行推理
bboxes, labels, _ = detector(img)
# 使用阈值过滤推理结果,并绘制到原图中
indices = [i for i in range(len(bboxes))]
for index, bbox, label_id in zip(indices, bboxes, labels):
[left, top, right, bottom], score = bbox[0:4].astype(int), bbox[4]
if score < 0.3:
continue
cv2.rectangle(img, (left, top), (right, bottom), (0, 255, 0))
cv2.imwrite('result.jpg', img)
microsoft/onnxruntime: 是一个用于运行各种机器学习模型的开源库。适合对机器学习和深度学习有兴趣的人,特别是在开发和部署机器学习模型时需要处理各种不同框架和算子的人。特点是支持多种机器学习框架和算子,包括 TensorFlow、PyTorch、Caffe 等,具有高性能和广泛的兼容性。
最近提交(Master分支:1 个月前 )
1bda91fc
### Description
Fixes the problem of running into failure when GPU inputs shuffled
between iterations. 9 天前
52a8c1ca
### Description
Enables using the MLTensor to pass data between models.
### Motivation and Context
Using MLTensor instead of ArrayBuffers reduces the number of copies
between the CPU and devices as well as the renderer and GPU process in
Chromium. 10 天前
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献11条内容
已为社区贡献11条内容







所有评论(0)